Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (ABC Model)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (ABC Model) could be described as “as I think, so I feel (and do)!” (The link is to Learning cognitive-behavior therapy: an illustrated guide By Jesse H. Wright, Monica Ramirez Basco, Michael E. Thase.) Understanding it is as simple as A B C.
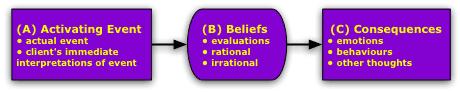
Activating Event – the actual event and the client’s immediate interpretations of the event
Beliefs about the event – this evaluation can be rational or irrational
Consequences – how you feel and what you do or other thoughts
Activating Event – the actual event and the client’s immediate interpretations of the event
Beliefs about the event – this evaluation can be rational or irrational
Consequences – how you feel and what you do or other thoughts
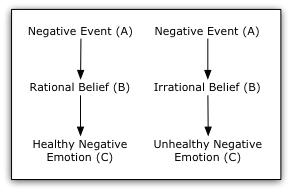
In the charts above and below (from counselingresource.com) you can see how that when a negative event happens, one can interpret it positively or negatively. How one interprets it affects how one feels, thinks and behaves.

*****
“Founder”: Aaron T Beck (1921 - )
"The stronger person is not the one making the most noise but the one who can quietly direct the conversation toward defining and solving problems."
*****
“Founder”: Aaron T Beck (1921 - )
"The stronger person is not the one making the most noise but the one who can quietly direct the conversation toward defining and solving problems."
*****
Examples

Situation One – Negative Perspective
A - Mary is walking down the street, and her friend Sarah walks right on by.
B – Mary thinks, “Oh Sarah is such a jerk.”
C – Next time, Mary ignores Sarah.
The “B” may or may not be true. Here is another possibility.
Situation Two – Positive Perspective
A - Mary is walking down the street, and her friend Sarah walks right on by. B – Mary thinks, “Oh that Sarah, always distracted.”
C – Mary calls out, Sarah apologizes for missing her, and they go for coffee!
As you can see, the role of the counselor in cognitive behavioral therapy is to challenge false beliefs – what I call ...
A - Mary is walking down the street, and her friend Sarah walks right on by.
B – Mary thinks, “Oh Sarah is such a jerk.”
C – Next time, Mary ignores Sarah.
The “B” may or may not be true. Here is another possibility.
Situation Two – Positive Perspective
A - Mary is walking down the street, and her friend Sarah walks right on by. B – Mary thinks, “Oh that Sarah, always distracted.”
C – Mary calls out, Sarah apologizes for missing her, and they go for coffee!
As you can see, the role of the counselor in cognitive behavioral therapy is to challenge false beliefs – what I call ...
The Lies We Tell Ourselves
These distortions in our thinking including:
1. Black-and-White - Thinking or either / or thinking.
2. Making Unfair Comparisons – usually in the negative
3. Filtering – honing in on the negative, forgetting the positive.
4. Personalizing - The Self-Blame Game
5. Mind-Reading – thinking we know what others think (negatively)
6. Catastrophising – imagining the worst case scenario
7. Overgeneralising – “I always mess up…”
8. Confusing Fact with Feeling – “If I think or feel this way then my thoughts/feelings must be correct'.
9. Labelling – I’m a loser vs. I made a mistake.
10. 'Can't Standitis' – being unnecessarily intolerant
1. Black-and-White - Thinking or either / or thinking.
2. Making Unfair Comparisons – usually in the negative
3. Filtering – honing in on the negative, forgetting the positive.
4. Personalizing - The Self-Blame Game
5. Mind-Reading – thinking we know what others think (negatively)
6. Catastrophising – imagining the worst case scenario
7. Overgeneralising – “I always mess up…”
8. Confusing Fact with Feeling – “If I think or feel this way then my thoughts/feelings must be correct'.
9. Labelling – I’m a loser vs. I made a mistake.
10. 'Can't Standitis' – being unnecessarily intolerant
Sample Session
In Sample Session Five, counselor Joan took a more direct approach with client Mary. Joan has the luxury of being able to confront Mary – to "take the gloves off" regarding Mary’s treatment of her own self – and know that if the client doesn’t agree, she can vote with her feet. Friends and partners can’t do that.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or any kind of professional and/or compassionate counseling is not about pretending problems don't exist. Rather, it’s about being more accurate about strengths and resources and enlisting these to make the changes necessary to live a good life on a number of levels.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or any kind of professional and/or compassionate counseling is not about pretending problems don't exist. Rather, it’s about being more accurate about strengths and resources and enlisting these to make the changes necessary to live a good life on a number of levels.
Further Reading and Video
Books
"The Cognitive Theory of Depression" by Aaron T. Beck, Guilford Press, 1979
"The Feeling Good Handbook" by David D. Burns, Avon Books, 1999
Aim for success, not perfection. Never give up your right to be wrong, because then you will lose the ability to learn new things and move forward with your life. Remember that fear always lurks behind perfectionism. Confronting your fears and allowing yourself the right to be human can, paradoxically, make yourself a happier and more productive person.
– David Burns
Video on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GqW8p9WPweQ
"The Cognitive Theory of Depression" by Aaron T. Beck, Guilford Press, 1979
"The Feeling Good Handbook" by David D. Burns, Avon Books, 1999
Aim for success, not perfection. Never give up your right to be wrong, because then you will lose the ability to learn new things and move forward with your life. Remember that fear always lurks behind perfectionism. Confronting your fears and allowing yourself the right to be human can, paradoxically, make yourself a happier and more productive person.
– David Burns
Video on Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GqW8p9WPweQ
One of the most striking differences between a cat and a lie [especially the lies we tell ourselves] is that a cat has only nine lives. - Mark Twain